Q & A
Problem using Uber-menu and a child theme of 2012. Menus are an issue for responsive design; the CSS for the mega-menus is probably not responsive.
Question about using S2 Member. Membership plugins can be hard to set up: there are lots of elements.
If you want to sell downloads of ebooks, use Easy Digital Downloads from Pippins Plugins.
Check out the Shoestrap framework (based on Twitter bootstrap).
WordPress plugin for mobile detection: WP Mobile Detect. You can use shortcodes in your content to decide what goes into your mobile site.
Modernizr JavaScript library detects features of mobile browsers. Ady says that IE earlier than 8 does not support media queries. http://caniuse.com/ and html5please.com are resources for cross-browser compatibility and fallbacks.
border-box defines the width of your box, including your padding, and the content shrinks to match the padding.
Declare it like this:
@media screen {
*, *: after, *:before {
-webkit-box-sizing: border-box;
-moz-box-sizing: border-box;
box-sizing: border-box;
}
Chris Pederick Web Developer Extension for Firefox and Chrome
Notes from Anca’s Presentation: Make Your WordPress Theme Responsive
You have to make more decisions than when making a non-responsive design.
Use CSS and sometimes JavaScript to hide, move, and resize elements.
Demo of the “Responsive” theme, showing the way the menu changes and the way the widgets stack.
CSS Tricks, a fluid-responsive site which starts to change as soon as you readjust the browser. This requires lots of math.
News Theme from StudioPress
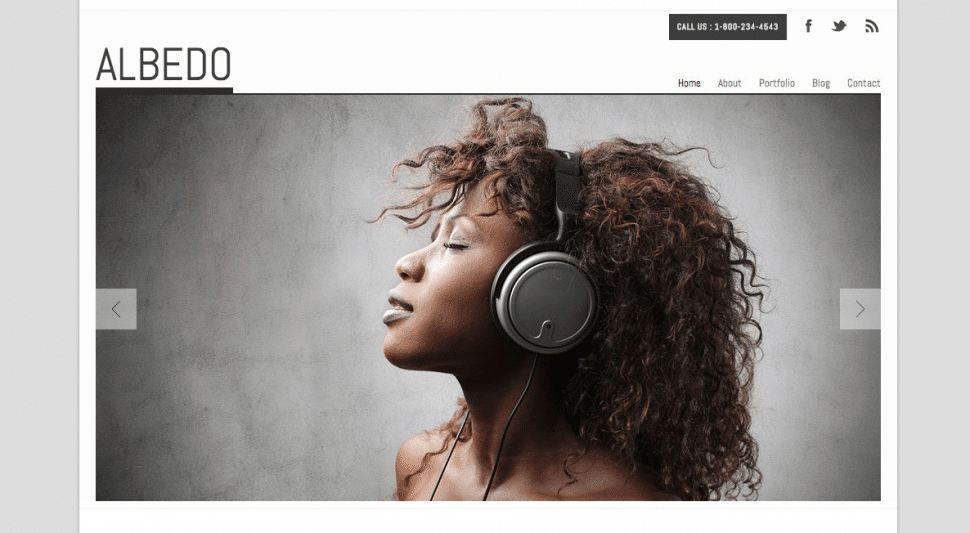
Albedo from Graph Paper Press reduces the number of portfolio items and blog posts it shows, keeping them the same size until you get to 320 px
Lots of websites are starting to be tablet-optimized (“You can’t find anything from 10 days ago, but it looks awesome on your iPad”)
Put your most important content at the top. Of the site, not the sidebar, if the sidebar is going to go to the bottom.
Draw boxes for your information hierarchy. Think about what will always be in view, even on the phone.
Breakpoints: the screen width at which the layout changes. Typically 240, 320, 480, 650, 800, 960. (Not everyone goes as small as 240, and not all themes choose the same breakpoints.)
Only some themes can be made responsive. Your HTML has to be in the right order.
Note: background images will not scale. (Images in divs will scale: you can set their widths at %.)
Widgets need to contain responsive elements. Some plugins generate non-responsive widgets or other elements, e.g. slideshows.
Embeded videos with hard-coded sizes won’t work. Anca thinks that WP oEmbeds should work. There is a tutorial on responsive YouTube embeds.
For SEO, you want the most important stuff near the top.
How much longer does it take to build a reponsive site? At least 25% more time, but not as much as twice as much.
Looking at stylesheets:
Responsive Theme has a nicely-documented CSS file. They use max-widths for their media queries: 980, 650, 480, 320, 240. The difference from something like Twenty Twelve is they use a grid.





Leave a Reply